The Difference Between POC and MVP: A Detailed Explanation
Summary
Introduction
In the world of product development, the terms POC (Proof of Concept) and MVP (Minimum Viable Product) are often used, but they refer to very distinct stages in the life cycle of a product. Understanding these differences is crucial to the success of any technology project. This article aims to explain these two concepts in depth and clarify their respective roles and importance.
What is a POC (Proof of Concept)?
The Proof of Concept, or Proof of Concept in French, is a preliminary achievement to demonstrate that an idea, theory or method is feasible. This is an exploratory step used to check the technical feasibility of an idea before developing it further.
POC Objectives
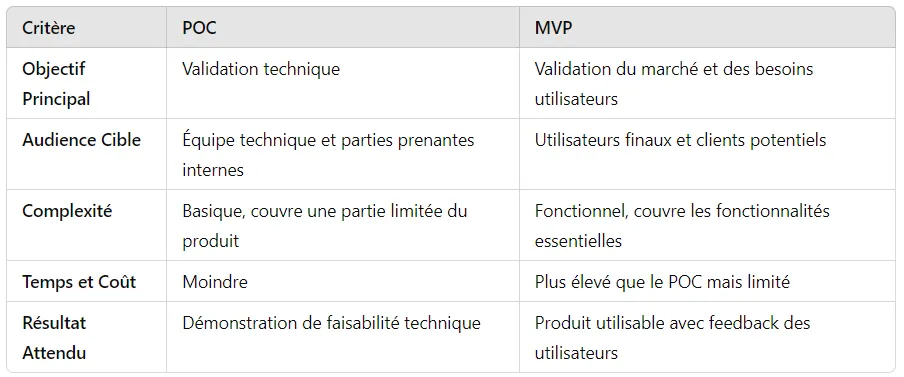
- Technical Validation: Ensuring that the planned technology works as intended.
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential technical obstacles and determine if they can be overcome.
- Demonstration to Stakeholders: Provide tangible proof that the concept can work, which can help secure funding or support from decision-makers.
Characteristics of the POC
- Simplicity: The POC is often very basic and only covers a limited part of the final product.
- Reduced Time and Cost: Developing a POC generally requires less time and resources than the full product.
- Focused on Technical Viability: The POC is not intended for use by end users, but only to prove that the idea is technically possible.
What is an MVP (Minimum Viable Product)?
The Minimum Viable Product is a product with just enough functionality to be used by early customers who can then provide feedback for future development. The goal is to launch a product with the minimum functionality necessary to meet user needs and test market hypotheses.
MVP Goals
- Market Validation: Test whether the product meets a real market need and whether there is demand for this product.
- User Feedback: Collect feedback from real users to improve the product.
- Risk Reduction: Minimize financial risks by avoiding developing features that are not needed or desired by users.
MVP Features
- Essential Features: Contains only the essential features to solve the users’ main problem.
- Usable by End Users: The MVP must be complete enough to be used and evaluated by the first customers.
- Iterative: Based on user feedback, the MVP is gradually improved and extended.
Comparaison entre POC et MVP
When to Use a POC or MVP ?
Use a POC when :
- You have an innovative idea and you are not sure of its technical feasibility.
- You want to demonstrate a new technology or concept to investors or stakeholders.
- You want to assess technical risks before committing to large-scale development.
Use an MVP when :
- You have validated the technical feasibility of your idea and you are ready to test the market.
- You want to launch a product quickly to get feedback from real users.
- You are looking to minimize costs by only developing essential features at the start.
Conclusion
POC and MVP are two crucial but distinct stages in product development. The POC ensures that the idea is technically feasible, while the MVP allows you to test the product on the market and collect valuable feedback for its improvement. Understanding when and how to use these tools can greatly increase your project’s chances of success.
In summary, POC focuses on the question “Can it work?” while the MVP focuses on “Does this solve a problem for users?”. By mastering these concepts, you can more effectively navigate your product development cycle, from initial idea to market launch.